Sales Line 954-266-0423
Service Line 888-265-7124
Sales Line 954-266-0423
Service Line 888-265-7124
What does tinnitus sound like? For those impacted, it can range from a faint high-pitched tone to a jarring buzz. Each person’s experience is distinct, and deciphering these sounds is key to understanding and managing tinnitus. Continue reading to uncover what these sounds may indicate and how to tackle them.
Tinnitus, while often described as ringing in the ears, is a phantom symphony that plays a variety of sounds, each as unique as the person experiencing them. From the consistent high-pitched ringing to the occasional buzz or hiss, tinnitus seems to have an orchestra of its own. These sounds, whether tonal or atonal, can hint at different underlying issues, painting a complex picture of this auditory phenomenon.
The first step to understanding and managing tinnitus is to decode this tapestry of sounds, especially for those who may develop tinnitus in the future, and reclassify tinnitus sounds accordingly.

Imagine the shrill whistle of a boiling kettle, incessant and demanding. This high-pitched ringing, often associated with a loud noise, is the soundtrack of tonal tinnitus, representing one of the most common tinnitus sound sensations described by those with tinnitus.
This ringing is more than just a bell; it serves as a constant reminder of the silent battle within the ear.

If you’ve ever been caught between radio stations, you are familiar with the cacophonous symphony of static noise. For some tinnitus sufferers, this is their everyday reality. Buzzing and hissing sounds, akin to electrical noise or chattering cicadas, are common descriptions of their tinnitus.
The hissing sound of tinnitus can resemble what tinnitus sound like when a tire is deflating.
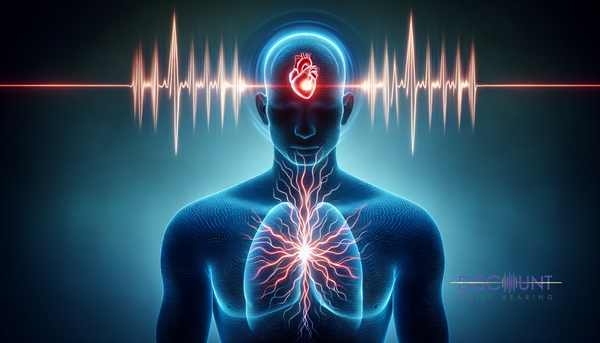
Tinnitus doesn’t always ring or buzz. Sometimes, it pulses. Known as pulsatile tinnitus, this form of tinnitus presents as rhythmic sounds aligning with the individual’s heartbeat. From soft whooshes to louder thumps, these sounds can vary in pitch and intensity, pushing the boundaries of what we understand tinnitus to be.
Tinnitus is not a one-size-fits-all condition. It manifests differently, with some experiencing symptoms briefly (acute tinnitus) and others dealing with it over extended periods (chronic tinnitus). It’s vital to comprehend these differences to grasp the duration and impact of tinnitus on individuals’ lives.
Chronic tinnitus is the unwelcome guest that overstays its welcome. For nearly a third of American adults with tinnitus, symptoms persist nearly constantly, interfering with concentration and masking natural sounds. This constant presence can lead to a decline in the overall well-being of sufferers, making peace and quiet a distant memory.
Acute tinnitus is like an unwelcome surprise, often following exposure to loud noises and usually resolves without intervention. It can last from a few minutes to several weeks, making its presence felt in the most inconvenient of times. It’s a reminder of how delicate our auditory system is and how everyday activities can have a significant impact on our hearing health.
Is improving your hearing with Phonak hearing aids on your mind? You're exactly where you need to be. In this blog, we'll unpack the world of Phonak hearing aids, covering everything from their costs and various models to comparisons with alternative brands and strategies for leveraging your investment effectively. Thanks to Phonak's state-of-the-art technology and adaptable solutions, a superior hearing experience is within reach.
Tinnitus triggers can be like a jigsaw puzzle, with each piece representing a potential trigger. Some common triggers include:
Understanding these triggers can help you manage your tinnitus and reduce its impact on your daily life.
Effective management of this condition can be achieved by recognizing these triggers.
Everyday sounds, whether it’s the roar of a concert or the hum of a hairdryer, can amplify external noises and trigger or intensify tinnitus symptoms. This reactive tinnitus, as it’s known, can make normal environments feel like acoustic minefields, with the simplest of noises causing distress.
Somatic tinnitus, triggered or changed by muscle movements in the face, head, jaw, or neck, adds another layer to the tinnitus puzzle. Strain or tension in these areas can inadvertently increase intracranial pressure and consequently pressure on the ears, triggering tinnitus.
Tinnitus is more than just an auditory condition – it’s an emotional one too. It can lead to anxiety, irritability, depression, sleep disruption, and issues with communication.
The emotional toll of tinnitus can be as challenging, or even more so, than the auditory symptoms.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a powerful tool for managing tinnitus. It helps patients alter their perception of their condition and tackle emotional reactions.
CBT reduces the distressing effects of tinnitus and facilitates habituation by encouraging patients not to fixate on their condition.
Sound therapy uses pleasant or calming sounds to diminish the presence of tinnitus and provide relief. Some examples of natural sounds that offer a soothing escape from the relentless sounds of tinnitus include:
These sounds can help mask the ringing or buzzing in the ears and promote relaxation.
Effective management begins with a diagnosis, which often requires a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and a physical examination.
Our goal is to reveal and help people hear phantom sounds of objective tinnitus concealed by silence, allowing them to better understand their perceived sound.
Audiologists play a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing tinnitus. They conduct specialized tests to determine the pitch and loudness of the tinnitus. By asking patients detailed questions about the characteristics of their tinnitus, audiologists can explore potential causes and guide them through the necessary hearing tests.
Ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists can provide a more comprehensive examination of tinnitus. They conduct a thorough medical history review and physical examination of the auditory system, including checking for any signs of an ear infection. If an underlying cause of tinnitus is suspected, they may recommend further imaging tests.
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for tinnitus, various treatment options can help manage the symptoms. Some common treatments include:
These treatments, known as sound therapies, aim to provide relief and restore the sounds of silence.
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) is one such treatment option for treating tinnitus. It combines directive counseling and acoustic therapy to encourage the habituation of tinnitus.
TRT aims to improve patients’ quality of life by minimizing the irritation and awareness of tinnitus sounds.
Maintaining a detailed record of your tinnitus experiences could significantly improve condition management. Discovering patterns through documenting episode frequency, intensity, and triggers could contribute to treatment planning.
A tinnitus diary can be a powerful tool in your tinnitus management arsenal. It helps uncover patterns and document the characteristics of each tinnitus episode.
This meticulous record-keeping can yield vital insights into understanding and managing the condition.
In the age of smartphones, managing tinnitus is just a tap away. Apps offer tools for tracking symptoms, managing sleep, and providing relaxation techniques to help reduce tinnitus-related stress. By combining multiple therapeutic strategies, these apps offer a comprehensive approach to tinnitus management, including smartphone sound generators.
We’ve journeyed through the world of tinnitus, from its many sounds to the emotional toll it can take. We’ve explored different triggers, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options. While tinnitus remains a complex and varied condition, understanding and managing it is possible. And remember, you’re not alone on this journey consult a hearing care professional like Discount Daily Hearing for questions today!
You can recognize tinnitus when you hear sounds without any external source, often described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, varying in volume.
Normal tinnitus can sound like ringing, hissing, roaring, crickets, screeching, sirens, whooshing, static, pulsing, ocean waves, buzzing, clicking, dial tones, and even music.
The three sounds of tinnitus are roaring, buzzing, and hissing. You can receive evidence-based treatment for these symptoms at The Tinnitus Clinic.
Tinnitus can be caused by various factors such as high blood pressure, allergies, anemia, or serious conditions like tumors or aneurysms, while other risk factors include TMJ disorder, diabetes, and head injury. It's important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation.